Git Branches
Branches let you work on different versions of a project without affecting the main code. This is useful for experimenting, fixing bugs, or building new features safely.
Introduction
When you’re working on a project, you often want to make changes or try new ideas without affecting the current working version. Git lets you do this by using branches. A branch is like a separate workspace where you can try out changes. Later, you can bring those changes back into the main project by merging or rebasing.
By default, Git starts with one branch, usually called main. This is what most beginners or small projects use. When you create a new branch, it copies the current state of the project and lets you build from there.
Terminology
Here are some key terms related to branching:
- Branch: A separate line of development in your Git repository.
- Main: The default primary branch in most Git projects.
- Feature branch: A branch created to work on a specific feature or change.
- checkout: The command used to switch between branches.
- Merge: Combines the changes from one branch into another.
- Rebase: Moves commits from one branch onto the end of another, creating a linear history.
When to use Branches
Branches are useful anytime you want to make changes without affecting the main code:
- Add a new feature: Create a feature branch while developing.
- Fix a bug: Make a debug branch so you can test without breaking other code.
- Experiment: Try something new without worrying about damaging the current project.
How to Branch
Creating Branches
When you create a new branch, Git creates a pointer or reference to the current commit. Any new commits you make on that branch stay separate from the main branch. You can switch between branches at any time using git checkout or the git switch command.
git checkout can create a new branch called and switch you to it. Here’s how to create and switch to a new branch:
$ git checkout -b [branchname]
You can see all branches in your repository with:
$ git branch
You can also check all branches on the GitHub repository page. This can be found in the dropdown pictured below:
In this menu, you can create a branch by typing a new branch name into the search bar. The option to create a new branch will appear as below:
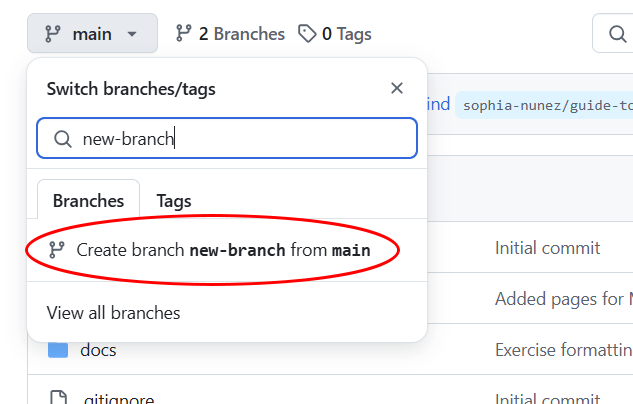 Click the option circled in red to create a branch with the name entered.
Click the option circled in red to create a branch with the name entered.
Combining Branches
Once you’ve completed making changes and are done with the branch, you can either merge it back into main or rebase your changes. For more information on the rebasing and how it differs from merging, check out our Rebase page.
To merge, using the following command:
$ git checkout main
$ git merge [branchname]
To rebase your changes, use:
$ git checkout main
$ git rebase [branchname]
Following either of these commands, push your updated branch using:
$ git push origin [branchname]
Depending on the project structure or management, you may need to submit a pull request rather than directly merging or rebasing. Check out our page on Pull Requests for more information!